|
WindsOfChange slideshow
|

|
|
|
|
Danish Turbine makes 1975 - 1985
The order, in which Turbines are listed, does not necessarily indicate a chronological order.
Make |
Years in production |
Riisager møllen |
|
 |
| Type: |
22 |
30 |
45 |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
10.2 |
12.5 |
14.5 |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
- |
- |
48 |
| Power [kW] |
22 |
30 |
45 |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
Stall |
| Blade Make |
Own |
Own |
Own |
| Turbines prod. |
10 |
10 |
8 |
Prototype machines of 17 kW, 37 kW and 55 kW were also developed. In 1978 an experimental 11 kW Turbine was installed at a telephone relay station at Nees, Jutland - for charging the stations "no break" batteries in case of a black out.
Christian Riisager was a carpenter. He was inspired by Johannes Juul's Gedser Turbine design, and used the same basic design for his turbine: 3 Blade upwind Rotor, driving an asynchronous induction generator - controlled by blade Stall. No airbrakes were installed on the first models. The first 2 Turbines were sold in 1976 to Carsten Fritzner and Torgny Møller.
His wife Boe, was also involved in the company. The Riisager machine was the first to be grid-connected in the new Danish wind era in the seventies.
In 1979 Chr. Riisager and his design became part of the new Windmatic Company. (His early partner Erik Nielsen in Herning, fabricated his own turbine line, named ERINI - with Steel blades.)
In 1983 Chr. Riisager stopped collaboration with Windmatic and worked on a turbine at Oxholm, in northern Denmark. Later he moved to Faroe Islands in the Atlantic Ocean, where he built up a turbine production with the local Governement.
More information on the 55/90/110/130 kW series fabricated at Faroe Islands.
After a short period of illness, Christian Riisager sadly passed away in month of June 2008, at the age of 78. He continued working in his carpenter workshop until his death. We, in the wind industry, are thankfull for what Christian did for wind power in his early pionering work.
|
 | Riisager small Turbine at Skærbæk, Riisager 22 kW at Torgny Møller – Wind Power Monthly, Riisager 22 kW at Rimmerhus, Riisager Oxholm 45 kW at RISØ |
|

|
Adolphsen Møllen |
|
 |
| Type: |
SA-11 |
SA-18 |
- |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
- |
- |
- |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
|
|
|
| Power [kW] |
11kW |
18kW |
- |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
- |
| Blade Make |
Økær |
Økær |
- |
| Turbines prod. |
7 |
? |
- |
On November 26th 1977 the first set of Økær blades was delivered to Svend Adolphsen. Svend was an electrician and mechanic, and had a small shop. He was very innovative. Turbine on the photo is the prototype with 4.5 m blades. The following turbines used 5 meter blades.
For more information see the Blade Story. |
 | Adolphsen prototype at Knudstrup on 6 m lattice tower, Prototype raised to 18 m, Adolphsen 11 kW serial production Turbine with Økær 5 m blades at Poul Jensen in Låsby |
|
|
|
|
 |
| Type: |
10 |
- |
- |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
5.7 |
- |
- |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
- |
- |
- |
| Power [kW] |
10kW |
- |
- |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
-l |
- |
| Blade Make |
Own |
- |
- |
| Turbines prod. |
34 |
- |
- |
The S.J. Wind Power, and later GSS Powermills - Rose – here pictured in test at RISØ Test Station near Copenhagen, was not grid-connected. It produced electricity for household hot water supply, using a heating element immersed in a storage tank. Blades in Poly Urethane Foam. (Integral Foam). Many S.J. Roses lost most of their blades in Hurricanes, but still a few S.J. Turbines are running in Denmark, 25 years later.
Key person: Svend Jensen |
 | Svend Jensen Turbine in test at RISØ Test Station |
|
|
Erini |
|
 |
| Type: |
22 |
45 |
- |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
13.6 |
- |
- |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
- |
- |
- |
| Power [kW] |
22kW |
45kW |
- |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
- |
| Blade Make |
Own |
Own |
- |
| Turbines prod. |
2 |
? |
- |
ERINI company was owned by Blacksmith Erik Nielsen, Herning, who was a former sub supplier to Christian Riisager. Erini used welded Steel blades for his own turbine design, but he used the same basic design as chosen by Riisager, inspired by Johannes Juul's GEDSER design. |
 | Erini Turbine in1985 |
|
|
Herborg Vindkraft |
SURVIVOR/Origin of Vestas Design
1977 - 1982
|
 |
| Type: |
HVK (22)/30 |
HVK 37 |
HVK 55 |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
10.6 |
12 |
15.6 |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
|
|
|
| Power [kW] |
(22)/30/5.5 |
37/7.5 |
55/11 |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
Stall |
| Blade Make |
Økær 5 |
Økær 6 |
Økær 7.5 |
| Turbines prod. |
8 |
2 |
1 |
Turbine designed by Karl Erik Jørgensen and Henrik Stiesdal.
On July 1st of 1978, Økær Vind Energi delivered the first 5 m blades for the Herborg Vindkraft prototype.
The first prototype was 22 kW. The next 6 Turbines fabricated were 30 kW models.
Karl Erik sadly passed away on October 2nd 1982 after serious illness.
In 1979 Herborg Vindkraft entered into a license agreement with nearby company Vestas, who until then was most known for their farm equipment.
For more information about Herborg Vindkraft see Blade Story. |
 | The Family home of Karl Erik Jørgensen with selfbuilt wind rose and the Økær Vind Energi 5 meter blades no. 11, 12, 13 delivered July 1.st 1978 ready to mount – Blades mounted on the 22 kW Turbine, 30 kW HVK 10 Turbine at Bjerregaard Dunes, Installing the first 55 kW Turbine at Vestas, 37 kW Herborg Turbine at Fjalting at the Danish West Coast, 37 kW Herborg Turbine at the work shop and family home in Herborg. |
|
|
Kuriant |
|
 |
| Type: |
KE 11K |
KE 15K |
KE 18.5 |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
10 |
10.9 |
10.9 |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
- |
- |
- |
| Power [kW] |
11 |
15 |
18.5 |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
Stall |
| Blade Make |
Økær 5 |
Økær 5 |
Økær 5* |
| Turbines prod. |
19 |
? |
100 |
Total number of 15 kW and 18.5 kW Turbines was 100.
On August 29th of 1979, Økær Vind Energi delivered the first 5 m blades for the Kuriant prototype. The design was developed by Svend Adolfsen, based on the Adolfsen turbine. Adolfsen and Kuriant signed an agreement on November 9th 1979.
The Kuriant company was originally manufacturing strawbale trailers for farmers.
See also the Blade Story.
The Turbine was sold versioned as grid connected or condenser-magnetised generator for hot household water supply.
*In 1980 Kuriant started using KJ blades instead of Økær blades.
Key person: Alfred Christensen, Ulfborg
|
 | 2 Different Kuriant models |
|
|
|
SURVIVOR
1979 - |
 |
| Type: |
Vestas HVK 10 |
Vestas HVK 15 |
Vestas V15 |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
10 |
15.6 |
15.6 |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
- |
- |
- |
| Power [kW] |
22 & 30 |
55/11 |
65/- |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
Stall |
| Blade Make |
Økær 5 / Aerostar |
Økær 7.5 / Aerostar |
Aerostar |
| Turbines prod. |
3 |
179 |
975 |
| |
| Type: |
Vestas V 16 |
Vestas V 17 |
Vestas V17 |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
16 |
17 |
17 |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
- |
- |
- |
| Power [kW] |
55 |
90/- |
75/18 |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
Stall |
| Blade Make |
Own |
Own |
Own |
| Turbines prod. |
85 |
1073 |
284 |
| |
| |
| Type: |
Vestas V 17E |
Vestas V 23 |
Vestas V23 |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
17 |
23 |
23 |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
- |
- |
- |
| Power [kW] |
90 |
150 |
200 |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
Stall |
| Blade Make |
Own |
Own |
Own |
| Turbines prod. |
34 |
1 |
2 |
After 1986: |
|
|
|
| Type: |
Vestas V 19 |
Vestas V 20 |
Vestas V 25 |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
18.8 |
20 |
25 |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
42/25 |
- |
44/30 |
| Power [kW] |
90/19 |
100 |
200/30 |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
Pitch |
| Blade Make |
Own |
Own |
Own |
| Turbines prod. |
111 |
100 |
246 |
The Vestas company was a well reputed company fabricating farm equipment, hydraulic truck cranes and cooling systems. This undoubtly helped the sales of Turbines to Danish farmers.
In 1979 Vestas signed a license agreement with Herborg Vindkraft, which transferred the Herborg Vindkraft (HVK) design to Vestas.
Prior to this, Vestas had performed experiments with a 15 kW Biblade Darrieus Turbine. Engineer Leon Bjervig designed this sturdy Darrieus Turbine. Vestas was then producing Farm equipment, Truck-Cranes and cooling systems. Bjervig convinced Vestas, that this was an interesting working field and they carried out experiments with different Rotor concepts for the Turbine. In fall 1979 Vestas abandoned the Darrieus design and entered into a license agreement for a horizontal axis Turbine design developed by nearby Herborg Vindkraft (Karl Erik Jørgensen). For more information see Blade Story.
The 55 kW Vestas HVK 15 became the workhorse for their first sales in California in 1983 - 85. . In 1982 Vestas began development of their own blade make. The first design to use these blades were the V17 75 kW Turbine. For the 55 kW Turbines Vestas still used AeroStar 7.5 m blades in 1985.
Keypersons in the Wind Power branch of Vestas, in early years: Finn M. Hansen, Birger T. Madsen, Per Krogsgaard (Sales) and Jørgen Thirstrup Pedersen (Engineer).
From 1988 Vestas also developed pitch controlled turbines, starting with the 200 kW V 25.
Vestas Turbines developed in the next years:
1988 |
V25/27 |
150 kW |
1990 |
V27/29 |
225 kW |
1993 |
V39 |
500 kW |
1995 |
V42/44 |
600 kW |
1997 |
V47 |
660 kW |
2000 |
V52 |
850 kW |
Hereafter MegaWatt Turbines were designed.
Febrary 1989 Danish Wind Technology was merged with Vestas. The Vestas company name was, for a period, changed to Vestas, Danish Wind Tedchnology A/S. Later it became: Vestas Wind Systems A/S.
For Vestas, the interest in the merger was DWT's experience with "large machines" (See Volund and DWT below) . |
 | Vestas 30 kW Turbine, Installation of first Vestas HVK 55 kW Turbine at Lem ( 4 pictures), Vestas Darrieus Bi-plane Turbine at Lem with 55 kW Turbine, Vestas 55 kW Turbine on Tubular Tower, Vestas V 25 - 200 kW Turbine with Pitch Control. |
|
|
|
|
 |
| Type: |
WM 10S |
WM 12S |
WM 14S |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
10.2 |
12.5 |
14.5 |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
- |
- |
48 |
| Power [kW] |
22 |
30 |
45/50/55 |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
Stall |
| Blade Make |
Own* |
Own* |
Own* |
| Turbines prod. |
24 |
11 |
30 |
The 1. of May 1979 Windmatic began fabricating the Riisager design. The blades had a load carrying wood spar and fibreglass skin. Cavities were filled with Polyurethane foam. Blades were stayed. The blades had been fabricated for some years by LM Glasfiber as in the Riisager designed shapes.
*) In 1982 a new productline was added to the Windmatic family: The first blades designed by LM Glasfiber A/S was adapted, and also tubular (shell) towers were added to the line of lattice towers.
New designs of WM 15S (60 kw) Ø 15.5 m dia. and WM 19S (120 kW) Ø 19 m dia.
Also a 8 meter diameter 11 kW "Folkemølle" was designed for hot water production, without grid connection. |
| Type: |
75 |
99 |
130 |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
17 |
19 |
19.4 |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
- |
- |
- |
| Power [kW] |
75 |
99 |
130 |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
Stall |
| Blade Make |
LM |
LM |
LM |
| Turbines prod. |
83 |
74 |
13 |
| |
| Type: |
150 |
180 |
200 |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
22 |
22 |
23 |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
- |
- |
- |
| Power [kW] |
150 |
180 |
200 |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
Stall |
| Blade Make |
LM |
LM |
LM |
| Turbines prod.. |
1 |
2 |
5 |
.
Only Turbines erected in Denmark are listed!
In 1994 the California Energy Commission reported 176 Windmatic Turbines Installed in California with a capacity of 13.6 MW ( average 78 kW) |
 | Windmatic 55 kW Turbine, Elegant Windmatic Turbines owned by Swedish IKEA near Copenhagen, Windmatic Turbines on tripod towers. |
|
|
|
SURVIVOR / ORIGIN OF MICON DESIGN
1980 - |
 |
| Type: |
NTK 22 |
NTK 30 |
NTK 55 |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
11 |
11 |
16 |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
- |
- |
- |
| Power [kW] |
22/7.5 |
30/7.5 |
55/11 |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
Stall |
| Blade Make |
Økær 5 |
Økær 5 |
Økær 7.5 |
| Turbines prod. |
15 |
22 |
125 |
Only Turbines erected in Denmark are listed here. (More than 1000 turbines were installed in California.)
The first turbine developed, was the 22 kW machine. The prototype Turbine was - after a test period at the production facility at Balle - sold to Erik Grove-Nielsen's Father at Hejnsvig in 1981. It still operates, now 27 years later.
Nordtank was owned by CEO Thorkild Rørbæk Jensen. Foreman at the production was Peder Mørup. Engineer in the first years: Erik Ørum Nielsen.
An 11 kW model using Økær/AeroStar 3.5 m blades was also delivered in early years. ( Turbines produced = 14). A 65 kW model was developed on basis of the 55 kW design. Later 75 kW (n=6), 99 kW (n=42), 100 kW (n=1), 130 kW (n=78) and 145 kW (n=1). Next model was the 150 kW turbine from 1989. (n=221).
For some models Dutch STORK blades were used from 1986 through 198X. Later LM Glasfiber blades were used.
The NORDTANK company earlier produced Road Tank Vehicles, which explains the name. On the old logo an automotive tank is seen. From their experience with rolled tankers skin, they derived the tubular wind turbine tower, which very soon became more common in Denmark than lattice towers. Danregn Vindkraft (Bonus) adopted this design, and later also Vestas began fabrication of tubular towers for their turbines. For more information on Nordtank see also Blade Story.
Nordtank in 1995 became "Nordtank Energy Group", (NEG). In 1997 NEG merged with Micon and became NEG-Micon. Later NEG-Micon merged with Vestas. ( Vestas Wind Systems). |
 | The Nordtank 22 kW prototype sold to Erik Grove-Nielsen’s father Knud at Hejnsvig and installed here, 55 kW Nordtank in Danish landscape, Nordtank 100 kW Turbine at Ebeltoft Harbour, Row of 13 on shore 55 kW Nordtank Turbines |
|
|
|
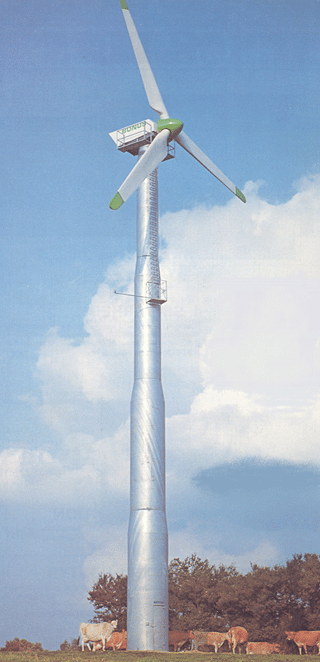
SURVIVOR (Now SIEMENS)
1980 - |
 |
| Type: |
22 |
30 |
55 |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
10.2 |
10.2 |
15.2 |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
- |
- |
- |
| Power [kW] |
22/5.5 |
30/5.5 |
55/11 |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
Stall |
| Blade Make |
Økær 5 |
Økær 5 |
AeroStar 7.5 |
| Turbines prod. |
3 |
11 |
96 |
Export models: |
|
|
|
| Type: |
25 |
35 |
65 |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
10.2 |
10.2 |
15.2 |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
- |
- |
- |
| Power [kW] |
25/6 |
35/6 |
65/15 |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
Stall |
| Blade Make |
AeroStar 5 |
AeroStar 5 |
AeroStar 7.5 |
| Turbines prod. |
? |
? |
646 |
|
|
|
|
| Type: |
95 |
150 |
300 |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
19 |
23.8 |
31 |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
- |
- |
- |
| Power [kW] |
95 |
150 |
300 |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
- |
| Blade Make |
AeroStar 9 |
LM Glasf.11 |
LM Glasfiber |
| Turbines prod. |
155 |
539 |
193 |
From summer 1981 the Blade Make was AeroStar.
After the bankrupcy of the AeroStar manufacturer DCER, in 1986, blades were supplied by LM Glasfiber.
Danregn (= Danish Rain) originally fabricated irrigation equipment for Danish farmers. Son of the founder: Peter Stubkjær Sørensen together with Egon Kristensen in 1980 got the chance to start up a new area of production. The first turbine was the 22 kW. Økær Vind Energi delivered the first 5 m blades for Danregn Vindkraft in December 1980 - for their prototype. see also Blade Story. First engineer employed was Ejler Kristensen.
Later the product was named BONUS. In 2004/2005 Bonus was acquired by SIEMENS. The new name is now Siemens Wind Power.
The company is the only Danish Wind Turbine Company, that never had a bankrupcy. When the Californian Wind market collapsed in 1986, most other companies failed.
Bonus Turbines developed in the next years:
- |
- |
320 kW |
1989 |
Ø 35/37 |
450 kW |
1994 |
Ø 41 m |
500 kW |
1996 |
Ø 44 m |
600 kW |
1994* |
Ø 50 m |
750 kW |
1996 |
Ø 54 m |
1000 kW |
* = Prototype.
Hereafter MegaWatt Turbines were designed. |
 | Danregn 30 kW nacelle, Installation of Bonus 55 kW Turbine at RISØ, 55 kW at RISØ, 95 kW Bonus Turbine with tripod tower . (Aerostar 9 meter blades |
|
|
|
SURVIVOR
1983 - |
 |
| Type: |
MICON 55/11 |
M 65/13/US |
M108/US |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
16 |
16 |
19 |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
45/29 |
48 |
45 |
| Power [kW] |
55/11 |
65/13 |
108 |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
Stall |
| Blade Make |
AeroStar 7.5 |
AeroStar 7.5 |
AeroStar 9 |
| Turbines prod. |
22 |
538 |
> 1500 |
Also Turbines of 100 kW, 150 kW, 175 kW, 200 kW, 225 kW, 250 kW, 350 kW, 400 kW, 500 kW, 600 kW and 750 kW were produced.
Peder Mørup was foreman at the production facilities of Nordtank. He left Nordtank in 1982 to start up his own Turbine make.
The company was named Moerup Industrial Windmill Company, MICON A/S - or MICON Energy Systems. The turbine had many similarities with the Nordtank machine. He used subsuppliers to a much greater extend, than his competitors in Denmark, which allowed him to speed up deliveries to the Californian Wind Rush in the eighties, without building up the production capacity at MICON.
Peder's brother Erling Mørup also entered the company.
After a period of controversy the two brothers diverted in January 1986, forming two new companies: Wincon headed by Erling Mørup should take care of the sales, and Wenergy headed and owned by Peder Mørup was the manufacturer of the turbines. In 1987 Peder Mørup acquired total control of Micon. Since that time, he never spoke a word to his brother.
|
 | Micon 100 kW Turbine in foreground, Micon 108 kW Turbines in Palm Springs California, Micon 150 kW in Denmark |
|
|
|
1986 - 1988 |
 |
| Type: |
55 |
95 |
99 |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
18 |
19.6 |
21 |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
- |
- |
- |
| Power [kW] |
55 |
95 |
99 |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
Stall |
| Blade Make |
- |
- |
- |
| Turbines prod. |
1 |
7 |
- |
| |
| Type: |
M22 |
- |
- |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
9.8 |
- |
- |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
- |
- |
- |
| Power [kW] |
22 |
- |
- |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
- |
- |
| Blade Make |
LM* |
- |
- |
| Turbines prod. |
- |
- |
- |
Only Turbines erected in Denmark are listed.
Wenergy was setablished by Peder Mørup (Brother to Erling Mørup) in 1986.
The early types were equipped with AeroStar blades - untill AeroStar bankrupted in 1986/87.
|
 | Wenergy Turbine in Danish harvest landscape |
|
|
Wincon |
1986 - 2000 |
 |
| Type: |
55 |
95 |
99 |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
18 |
19.6 |
21 |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
- |
- |
- |
| Power [kW] |
55 |
95 |
99 |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
Stall |
| Blade Make |
- |
- |
- |
| Turbines prod. |
1 |
4 |
73 |
| |
| Type: |
200 |
250 |
600 |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
24/26 |
29 |
45 |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
- |
- |
- |
| Power [kW] |
200 |
250 |
600 |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
Stall |
| Blade Make |
- |
- |
- |
| Turbines prod. |
79 |
2 |
5 |
Export types: |
| Type: |
M22 |
M55/11 |
M100 |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
9.8 |
16 |
19 |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
- |
- |
- |
| Power [kW] |
22 |
55/11 |
108 |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
Stall |
| Blade Make |
- |
- |
- |
| Turbines prod. |
? |
? |
? |
Only Turbines erected in Denmark are listed. In 1994 the California Energy Commission reported 199 Wincon Turbines Installed in California with a capacity of 21.2 MW ( average 107 kW)
Wincon was etablished by Erling Mørup (Brother to Peder Mørup) in 1986.
The early types were equipped with AeroStar blades - untill AeroStar bankrupted in 1986/87.
Some Turbines were equipped with M.A.T. blades. (Micon Airfoil Technology) M.A.T. blades were designed by Helge Pedersen of RISØ. Emergency brake system was based on parachutes placed behind a hatch in the tip leeside.
A single 755 kW prototype (Ø 48 m) was fabricated in 1998.
|
 | Wincon Turbine with M.A.T. blades, Blades with employed parachute air brakes |
|
|
|
|
 |
| Type: |
T-1780 |
T-1995 |
- |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
17 |
19 |
- |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
53/40 |
- |
- |
| Power [kW] |
80/15 |
95/- |
- |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
- |
| Blade Make |
LM 8.2 |
- |
- |
| Turbines prod. |
25 |
23 |
- |
Only Turbines erected in Denmark are listed.
The Tellus company emerged, when engineers and other key employees from bankrupted Windmatic gathered, and formed a new company. Although the company had a short lifetime, their turbines were recognized for their superior quality, in design and fabrication.
Passengers arriving at Copenhagen Airport fly over a small windfarm at the end of one of the runways - these are Tellus Turbines. |
 | Tellus Turbine at RISØ Test Station, Tellus Turbine equipped with advanced aerodynamic test blade at RISØ. |
|
|
|
|
 |
| Type: |
HD1 |
HD2 |
- |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
5 |
10 |
- |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
- |
- |
- |
| Power [kW] |
5.5 |
22 |
- |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
-l |
| Blade Make |
Own |
Own |
- |
| Turbines prod. |
? |
? |
- |
Dana Vindkraft established 1977 by a.o. pioneers Claus Nybroe and Rio Ordell.
Claus Nybroe later established the company Windflower, designing and fabricating multiblade wind roses, using multipole PMG generators.
Claus Nybroe was co-author of an early very important textbook (handbook) on wind turbine construction (and solar as well). More information to follow.
|
 | Holger Danske HD2 Turbine from Dana Vindkraft – at Kolding Højskole |
|
|
|
|
 |
| Type: |
600 Watt |
2.2 kW |
4 kW |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
2 |
3.2 |
3.8 |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
- |
- |
- |
| Power [kW] |
0.6 |
2.2 |
4 |
| Power Regulation |
- |
- |
- |
| Blade Make |
Own |
Own |
Own |
| Turbines prod. |
16 |
3 |
5 |
The Windflower design and construction was made by Wind Veteran and Pioneer Claus Nybroe.
From 1986 - 1988 Claus cooperated with WINCON on development of Windflower design and tests.
Many models have been developed for remote area electricity production and for water pumping.
|
 | Windflower waterpumping Turbine in test at RISØ, Windflower Turbine at Thorup near Hundested – Denmark, 2 Windflower models in test at Claus Nybroes home at Stenstrup Funen |
|
|
|
|

|
| Type: |
SM 22 |
SM 30/SM45 |
SM 55 |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
10 |
12 |
14 |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
- |
- |
- |
| Power [kW] |
22 |
30/45 |
55 |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
Stall |
| Blade Make |
Own |
Own |
Own |
| Turbines prod. |
4 |
5 |
8 |
Bladeconcept is equal to Riisager and early Windmatic.
Most turbines had bladetips in green color.
Turbine fabricated at Sonebjerg Maskinfabrik, Kolding. |
 | Sonebjerg 55 kW Turbine in Danish landscape |
|
|
|
|

|
| Type: |
22 |
45 |
- |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
10.35 |
- |
- |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
- |
- |
- |
| Power [kW] |
22kW |
45kW |
- |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
- |
| Blade Make |
Own |
Own |
- |
| Turbines prod. |
18 |
? |
- |
Blades were fabricated in all wood.
Owner and founders of Kongsted Møllen, was Ole and Kenny Hansen of Kongsted, Sealand. Ole was an earlier customer to Chr. Riisager. (Riisager Turbine) Johansen felt that he could substantially enhance the turbine design, and so he did. In 1982 he halted the production.
|
 | Wood bladed Kongsted 22 kW Turbine at Sealand, Denmark |
|
|
|
|
 |
| Type: |
Poulsen |
Poulsen |
- |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
13 |
10.6 |
- |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
120 |
- |
- |
| Power [kW] |
30* |
15 |
- |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
- |
| Blade Make |
Own |
Own |
- |
| Turbines prod. |
5 |
5 |
- |
* A second generator of 5.5 kW was operating at low windspeeds (at lower r.p.m.).
Turbine was developed by Ulrik Poulsen and manufactured by VPF Maskinfabrik.
Blades in extruded aluminum. A popular name for this Turbine was “the Stork”, giving the impression of a Stork picking up Frogs in the Meadows.
A second model was developed: Here the rotor was placed on a nacelle at a conventional upright tower; much alike the American Storm Master.
|
 | Ulrik Poulsen Turbine MK I in test at RISØ, Ulrik Poulsen Turbine MK II |
|
|
|
|
 |
| Type: |
DVI 15/2 |
- |
- |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
9 |
- |
- |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
50 |
- |
- |
| Power [kW] |
15 |
- |
- |
| Power Regulation |
Pitch |
-l |
- |
| Blade Make |
Own |
- |
- |
| Turbines prod. |
- |
- |
- |
The GIROMILL was manufactured by Dansk Vindkraft Industri ApS ( Finn Wiinberg). (The rotor was designed by Danish Wind Veteran Flemming Rasmussen of RISØ. Flemming earlier worked with a Darrieus turbine at RISØ). The GIROMILL is not a Darrieus Turbine, and the Blade pitch is variable, and guided - during one revolution - by a Wind Vane through a central mechanical system.
Diameter of the Rotor is 9 meter. The length of each Aluminum Blade: 5.5 meter.
Generator 15 kW - Rotor running at 50 r.p.m. Pitching of the blades is used as Air Brake.
|
 | Giro Mill in test at RISØ Test Station |
|
|
|
|
 |
| Type: |
18 Sp |
- |
- |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
11 |
- |
- |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
- |
- |
- |
| Power [kW] |
18.5 |
- |
- |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
-l |
- |
| Blade Make |
KJ Fiber |
- |
- |
| Turbines prod. |
9 |
- |
- |
Odder Møllen was fabricated by Scandinavian Wind Systems LTD, located in the Town of Odder, South of Århus, and headed by NN.
The Odder Turbine had a standard Asynchronous generator, but the company also carried out experiments with a multipole (58) generator from Transmotor. (A Copenhagen company delivering generators for ships - Engineer Aage Larsen at Transmotor was a great help to many new manufacturers of stand alone turbines for household hot water production)
|
 | 2- Bladed Odder Turbine, 3-Bladed Odder Turbine |
|
|
|
1980 - |
 |
| Type: |
M-15 |
M-265 |
- |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
8 |
28.3 |
- |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
0 - 140 |
42/28 |
- |
| Power [kW] |
15 |
265/58 |
- |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Pitch |
- |
| Blade Make |
Own |
Own |
- |
| Turbines prod. |
1 |
1 |
- |
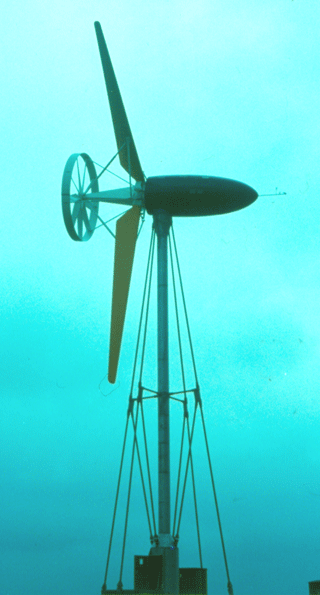
Both turbine types were downwind designs. The M-15 was 2-bladed.
The prototype was erected in southern Denmark (1982). No further turbines were erected. The Turbine was partly designed by Danish Wind Veteran Helge Petersen.
Special features: The Wind Rose Tail reduced the need for an active yaw system. (The tail was not Helges design!)The pitch hinges was designed and located so, as to use aerodynamic and centrifugal forces to enable an autonomic active safety system. Helge Petersen sadly passed away on January 7th 2010 at the age of 88.
The, somewhat special design did not attract many costumers. Only one Turbine of this design was manufactured.
The Turbine was a spinn-off from the 2 Danish 630 kW NIBE Turbines, erected by the Ministry of Commerce and the Electric Utilities in 1980. The production of bladeparts to the NIBE turbines gave VØLUND in Viborg a basic experience in bladeproduction techniques. VØLUND wanted to commercialise this knowledge.
VØLUND A/S had for many years been establishing Power Stations and major incineration plants world wide. The facility at Viborg was the earlier "Brødrene Christensens Beholdefabrik", which in the origin manufactured steel tanks for oil etc. As the facility also fabricateded storage tanks made of filament wound fibreglass, this company was chosen by the Ministry of Commerce, to fabricate the filament wound D-spars for the Nibe turbines. For further information on the Nibe turbines see European State turbines.
2 years later the company merged with other companies to Dansk Vind Teknik A/S.
|
 | Vølund 265 kW at Rejsby, Denmark. |
|
|
Danish Wind Technology DWT
|
1983 - |
 |
| Type: |
Windane 9 |
Windane 12 |
Windane 31 |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
9 |
12 |
30.8 |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
101 |
- |
42 |
| Power [kW] |
15 |
25/40/50 ! |
340(300) |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
Stall/Pitch |
| Blade Make |
Own |
Own |
Own |
| Turbines prod. |
1 |
2 |
7 (?) |
| |
|
|
|
| Type: |
Windane 34 |
Windane 40 |
- |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
34 |
40 |
- |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
- |
- |
- |
| Power [kW] |
400 |
750 |
- |
| Power Regulation |
Pitch |
Pitch |
- |
| Blade Make |
Own |
Own |
- |
| Turbines prod. |
89 |
5 |
- |
The Windane 9 and 5 was to be grid-connected or stand alone. Windane 12 was to be stand alone.
To my knowledge, the small turbines were only fabricated in prototypes.
Despite of it's poor visual design qualities, a number of the Windane 31 was sold for an onshore windfarm at Lynæs, Denmark. Later model were the 400 kW Windane 34 (1988) and 750 kW Windane 40 (1986) . 35 Windane 34 Turbines were installed in California in the eighties.
Corporate history: Dansk Vind Teknik (DVT) or Danish Wind Tehnology (DWT) was founded in 1981 at a venture of the parts: Vølund A/S, ASEA A/S and the Danish Ministry of Energy (and later SEAS, the utility company, that erected the GEDSER turbine.) ASEA was a Scandinavian manufacturer og elctric motors etc. Vølund is described above.
DWT performed poor, compared to companies like BONUS, Vestas and Nordtank.
Febrary 1989 Danish Wind Technology was merged with Vestas. The Vestas company name was, for a period, changed to Vestas, Danish Wind Tedchnology A/S. Later it became: Vestas Wind Systems A/S.
For Vestas, the interest in the merger was DWT's experience with "large machines". |
 | DWT 15 kW in test at RISØ, Inauguration of Wind Farm of DWT WD 31 Turbines at Lynæs, Sealand, WD 34 400 kW Turbine in test at RISØ, Row of WD 34 Turbines at Kappel, Denmark |
|
|
|
|
 |
| Type: |
90/95 |
120 |
150 |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
19.6 |
21 |
23.2/27/28 |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
- |
- |
- |
| Power [kW] |
90/95 |
120 |
150 |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
Stall |
| Blade Make |
LM |
LM |
LM |
| Turbines prod. |
2 |
3 |
172 |
| |
| Type: |
160/180 |
220 |
250 |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
23.2 |
25 |
29.2 |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
- |
- |
- |
| Power [kW] |
160/180 |
220 |
250 |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
Stall |
| Blade Make |
LM |
LM |
LM |
| Turbines prod. |
36 |
12 |
8 |
| |
| Type: |
500 |
600 |
750 |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
37 |
42 |
48/52 |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
- |
- |
- |
| Power [kW] |
500 |
600 |
750 |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
Stall |
| Blade Make |
LM |
LM |
LM |
| Turbines prod. |
22 |
44 |
4 |
Only Turbines erected in Denmark are listed.
The company was established at Skagen, and later moved to NørreSundby. In 1999 Wind World was sold to Nordtank Energy Group.
Key Persons in early years were the brothers: Karl Erik Olsen and Lars Olsen. |
 | Wind World Turbines |
|
|
|
|
 |
| Type: |
N17/75 |
N27/150 |
N27/250 |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
17 |
27 |
27 |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
- |
- |
- |
| Power [kW] |
75 |
150 |
250 |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
Stall |
| Blade Make |
KJ / LM |
KJ / LM |
LM |
| Turbines prod. |
1 |
203 |
57 |
Nordex Turbines developed and sold in the next years:
- |
Ø 29 m |
250 kW |
291 prod. |
1995 |
Ø 43 m |
600 kW |
538 prod. |
- |
Ø 46 m |
600 kW |
51 prod. |
1995 |
Ø 46 m |
750 kW |
1999 |
Ø 50 m |
800 kW |
132 prod. |
Hereafter MegaWatt Turbines were designed
Key designer in early years: Knud Buhl-Nielsen, who earlier cooperated with the Folkecenter (Smedemester design) and later designed the Lolland Turbine.
Key personnel were the brothers: Carsten and Jens Pedersen of Thyregod, only a few kilometres from "BONUS Capital" Brande.
First blade make used was KJ Fiber.
Later the headquarters of Nordex was moved to Germany.
|
 | 150 kW Nordex Turbine, 150 kW Nordex nacelle on ground |
|
|
|
|
 |
| Type: |
Danwin 19 |
Danwin 24 |
- |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
19.6 |
24 |
23.2 |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
- |
- |
- |
| Power [kW] |
99/110/140 |
150 |
180 |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
- |
- |
| Blade Make |
AeroStar 9 |
LM 11 |
LM 11 |
| Turbines prod. |
12 |
> 239 |
43 |
| |
| Type: |
- |
- |
- |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
24 |
27 |
- |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
- |
- |
- |
| Power [kW] |
200 |
225 |
- |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
- |
| Blade Make |
LM |
LM |
- |
| Turbines prod. |
30 |
15 |
- |
Key persons in Danwin were Engineers Per Lading and Thorkild Dahlgreen.
At least 233 Turbines were installed in the Californian Wind Rush of the eighties.
In 1994 the California Energy Commission reported 233 Danwin Turbines Installed in California with a capacity of 36.0 MW ( average 154 kW)
|
 | Danwin 100 kW with Aerostar 9 m Blades in test at RISØ, Danwin Turbine 150 kW Turbine with LM Blades in test at RISØ, Danwin Turbines in California Windfarm, Danwin 100 kW nacelle in shop. |
|
|
|
|
 |
| Type: |
200 |
250 |
- |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
25.5 |
25.5 |
- |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
- |
- |
- |
| Power [kW] |
200 |
250 |
- |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
- |
| Blade Make |
AeroStar 12 |
AeroStar 12 (?) |
- |
| Turbines prod. |
4 |
15 |
- |
Dencon was produced at the island of Ærø, at the shipyard of Ærøskøbing. The design was made by the Folkecenter (see grassroot section of Windsofchange), including engineers Henrik Kirchheiner and Peter Rasmussen, besides Preben Maegaard.
Initially the design was named: AeroDan, then Dencon and later Dancon.
(Also see ScanMill brochure attached)
Key persons: Bent T. Gregersen,
At least 19 Turbines were produced. |
 | Dencon 200 kW Turbine in Danish landscape, Row of Dencon 200 kW Turbines |
|
|
|
|
 |
| Type: |
10 kW |
- |
- |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
8 |
- |
- |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
|
|
|
| Power [kW] |
10 |
- |
- |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
- |
- |
| Blade Make |
KJ Fiber * |
- |
- |
| Turbines prod. |
> 5 |
- |
- |
Downwind turbine.
Blade for the prototype was delivered by Økær Vind Energi, but turbines in serial production had KJ Fiber blades.
Key person: Jørgen Hansen.
Household turbine for producing hot water. |
 | Kramsbjerg 10 kW Turbine in Danish landscape |
|
|
|
|
 |
| Type: |
22 |
60 |
100 |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
10.7 |
16.3 |
20.6 |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
73 |
47 |
36 |
| Power [kW] |
22 |
60 |
100 |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
Stall |
| Blade Make |
Økær 5 |
AeroStar 7.5 |
AeroStar 10 |
| Turbines prod. |
13 |
6 |
13 |
The SMEDEMESTER koncept was developed at the Danish FOLKECENTER (Run by Preben Maegaard) by a.o. engineer Knud Buhl Nielsen and the talented blacksmith Bendy Poulsen. The first model was a 22 kW turbine. Blades were ØKÆR VIND ENERGI 5 meter. The prototype was tested and proven by RISØ. The Drawings and specifications were made available to local blacksmiths all over Denmark. After some time several minor companies were manufacturing the 22 kW turbine according to the drawings made available by the Folkecenter. None of these companies got a long track record. Only Næsby Smedie, fabricating the Loland turbine.
A 500 kW and six 100 kW Turbines at Hanstholm were also named Smedmester. |
 | 22 kW Smedemester installation at RISØ - Rotor hoist, 22 kW Nacelle at show on the ground, The A.P. Smedemester Turbine, Smedemester mounted with Solid wood blades, Fasterholt Turbine. |
|
|
|
|
 |
| Type: |
22 |
60 |
100 |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
10.7 |
16.3 |
20.6 |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
73 |
47 |
36 |
| Power [kW] |
22 |
60 |
100 |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
Stall |
| Blade Make |
AeroStar 5 |
AeroStar 7.5 |
AeroStar 10 |
| Turbines prod. |
? |
? |
? |
For USA exports, 60 Hz versions of the 3 turbine designs were made: 33 kW , 75 kW and 120 kW. A talented senior design engineer on the project was Knud Buhl Nielsen, who later became the key engineer at the design of the Nordex turbines in Denmark and later Germany.
The Lolland turbine was the most succesfull example of the "Smedemester", and the only one that was sold to California in the Wind Rush days.
The turbine was produced by Blacksmith Davidsen of Næsby Smedie, at Lolland in southern Denmark. |
 | 100 kW Lolland Turbine in Danish landscape with Aerostar 9 m Blades, 60 kW Lolland Turbines in Tehachapi, California |
|
|
|
|
 |
| Type: |
KM-T 103 |
- |
- |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
(10) |
- |
- |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
- |
- |
- |
| Power [kW] |
11 |
- |
- |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
- |
- |
| Blade Make |
- |
- |
- |
| Turbines prod. |
15 |
- |
- |
The KM Turbine was delivered either as grid connected, or with a synchronuos generator coupled to an immersed heating element for hot water supply. Founder and owner was Engineer Kjeld Reinholdt Møller.
In the following years Reinholdt Møller developed a successfull 2-bladed Turbine called SWINGER. Rotor diameter 13 meter.
This Turbine later became the GAIA Turbine. |
 | 11 kW KM Turbine, 2-Bladed “SWINGER” Turbine |
|
|
|
|
 |
| Type: |
15 |
18.5 |
55 |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
10 |
10.7 |
16.7 |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
88 |
60 |
40 |
| Power [kW] |
15 |
18.5 |
55 |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
Stall |
| Blade Make |
KJ Fiber 5 |
KJ Fiber 5 |
KJ Fiber |
| Turbines prod. |
1 |
8 |
1 |
60 Hz versions of 22 kW and 65 kW for the US market was also marketed.
Prototypes for a 95 kW, a 150 kW and a 275 kW Turbine were fabricated in 1988-89. |
 | Reymo Turbine in Danish farmland |
|
|
|
|
 |
| Type: |
I |
- |
- |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
18 |
- |
- |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
51 |
|
|
| Power [kW] |
75kW |
- |
- |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
- |
-l |
| Blade Make |
LM Glasfiber |
- |
- |
| Turbines prod. |
? |
- |
- |
2 Generators 75 kW / 18.5 kW
Key person: Helge Petersen ( Not the Helge Petersen known from the Tvind turbine design and the early RISØ Test Station) |
 | Pademo Turbine in Danish landscape |
|
|
|
|
 |
| Type: |
- |
- |
- |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
19 |
22.2/23.6 |
23.6 |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
- |
- |
- |
| Power [kW] |
90 |
150 |
175 |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
Stall |
| Blade Make |
LM |
LM |
LM |
| Turbines prod. |
1 |
38 |
5 |
In 1990 a 300 kW prototype was erected but never came in production.
DWP or Danish Wind Power.
Key persons: Hans Ullersted and Aage Højbak. |
 | 150 kW Danish Wind Power in Danish farm land |
|
|
|
|
 |
| Type: |
- |
- |
- |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
22 |
22 |
26 |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
- |
- |
- |
| Power [kW] |
130 |
150 |
270 |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
Stall |
| Blade Make |
LM |
LM |
LM |
| Turbines prod. |
7 |
28 |
3 |
A 200 kW prototype was also fabricated.
Key person: Flemming Østergaard |
 | Vindsyssel 150 kW with early LM 11 m blades having Leading Edge Spoilers, Vindsyssel Turbine with solid wood blades |
|
|
|
|
 |
| Type: |
- |
- |
- |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
7 |
8 |
- |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
- |
- |
- |
| Power [kW] |
7.5 |
11 |
- |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
- |
| Blade Make |
- |
- |
- |
| Turbines prod. |
11 |
1 |
- |
. |
 | Thy Turbine in test at RISØ |
|
|
|
|
 |
| Type: |
18 kW |
22 kW |
- |
| Rotor Dia. [m] |
11 |
11 |
- |
| Rotor r.p.m. |
- |
- |
- |
| Power [kW] |
18 |
22 |
- |
| Power Regulation |
Stall |
Stall |
- |
| Blade Make |
KJ Fiber |
KJ Fiber |
- |
| Turbines prod. |
10 |
1 |
- |
When Kuriant stopped production in 1984 - The Kuriant design was marketed and manufactured by owner of Hjerm Elektro: Svend Erik Thusgaard - in the name "Bosted Møllen". |
 | 18 kW Bosted Turbine in Danish farm land |
|
|
| |
|
|